Laser Scanner Comparisons: 7 Capabilities to Check Before You Buy
With the proliferation of scanner types and brands, how can you determine which laser scanner is the best fit for your application? Here are seven capabilities to evaluate before you make your purchase.
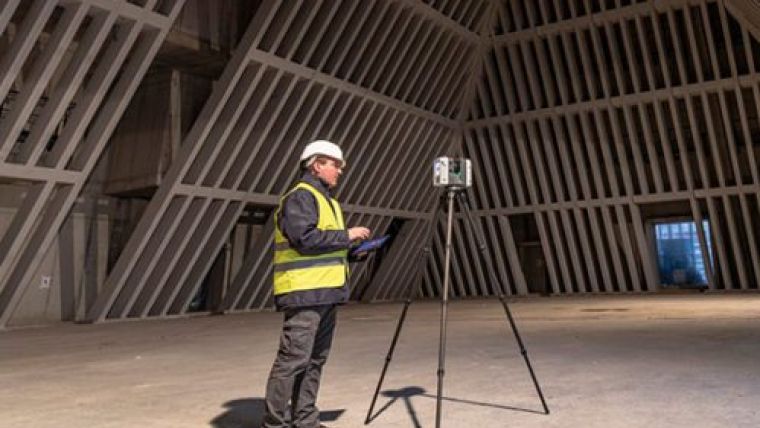
Surveying service providers are increasingly adding 3D laser scanning and other reality capture equipment to their technology toolbox, and for good reason. Laser scanners capture comprehensive data on buildings, infrastructure and environments through 360-degree images and millions of accurate measurement points collectively known as point clouds. This allows the captured data of various sites to be documented quickly and analysed directly in the field for QA/QC measures. But how can you determine which laser scanner is the best fit for your application? Here are seven capabilities to evaluate before you make your purchase.
As the popularity of the technology has accelerated, so, too, has the proliferation of scanner types and brands. A quick search online or in social media pulls up a number of different options, with various claims regarding speed, accuracy and quality. How can you determine which laser scanner is the best fit for your application?
A little knowledge on the key considerations in choosing a laser scanner can go a long way toward helping you make a wise investment that will make your company more efficient and more effective for years to come. Here are seven capabilities to evaluate before you make your purchase.
1. Scan speed and image capture
One or two million points per second sounds impressive, but, what does that mean in real-world terms? What happens to the scan speed when you want a full-dome image capture of a scene along with the scan data? What if you need full-dome High-Dynamic Range (HDR) imagery to see minute details in shadows or bright light conditions – how does that affect the speed of data capture?
Knowing the field performance of a highly rated laser scanner can be useful for comparison. For example, the Leica RTC360 3D laser scanner scans at two million points per second (pps) and captures a full-dome HDR image in one minute. This means you can complete a full high-resolution scan (3 mm) of your scene at a 10-metre range in less than three minutes with true HDR imagery. Running the scanner at maximum speed without HDR images allows you to complete scans in less than 30 seconds.
True vs. laser HDR: If you plan to use HDR as part of your scanning procedure to document your environment, be sure to check the source of the imagery. With real HDR imagery, high-resolution cameras collect high-quality source images that are overlapped so they can be blended together easily. Some laser scanners combine non–HDR imaging with laser intensity values to create more contrast in the colourised point cloud and a panoramic “HDR” image. While this approach can speed up HDR image capture in the field, it slows down processing in the office when working with the high–resolution scan data. Laser-based HDR images also lack natural colours, which can be important to the project.
When evaluating a laser scanner, look at how the scanning speed translates to the work you do every day.
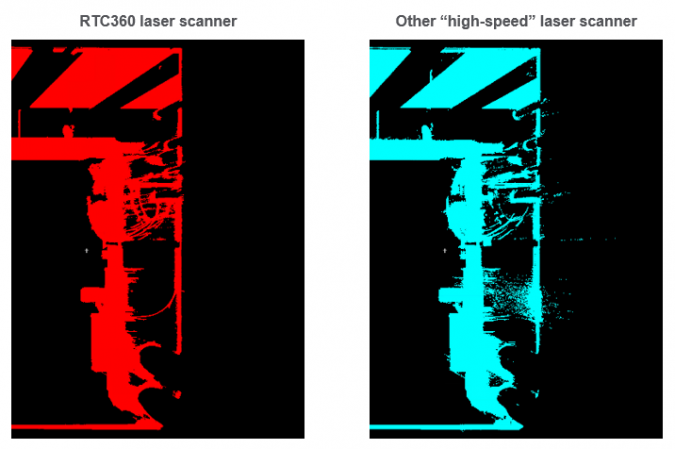
2. The data quality of the scans at high speed
Data quality is important, but it’s not always an easy parameter to measure when comparing laser scanners. To get an accurate assessment of data quality, ask for a high-resolution demo scan of an area at a 10-metre range that includes complex surfaces, and evaluate the data on the following key points:
Completeness. Is any data missing? Focus especially on areas where the angle of incidence is flat; the data should be just as complete here as in other areas of the scan.
Cleanliness. The data should be clean and crisp, with no invalid points “floating” in the scan data.
Geometric Accuracy. The geometry of scanned objects should be correct. Watch for rounded edges.
Range Noise. On some laser scanners, achieving clean, high-quality scan data with low range noise requires significantly slower scan speeds. A laser scanner is not really high speed if it takes hours to complete a high-quality scan. Check to see if the laser scanner requires you to determine the amount of noise acceptable in your data and then choose the corresponding quality setting. If so, be aware that this process will add time and affect the geometry of your resulting scans. A better approach is to use a laser scanner that delivers the best quality automatically, without adjustments and without compromising scan speed.
Value staying current with geomatics?
Stay on the map with our expertly curated newsletters.
We provide educational insights, industry updates, and inspiring stories to help you learn, grow, and reach your full potential in your field. Don't miss out - subscribe today and ensure you're always informed, educated, and inspired.
Choose your newsletter(s)